How Does a Computer Network Work? Basics Explained
Computer networks connect devices, enabling smooth communication and resource sharing1. These systems form the backbone of modern digital interactions. They support critical infrastructure across various sectors2.
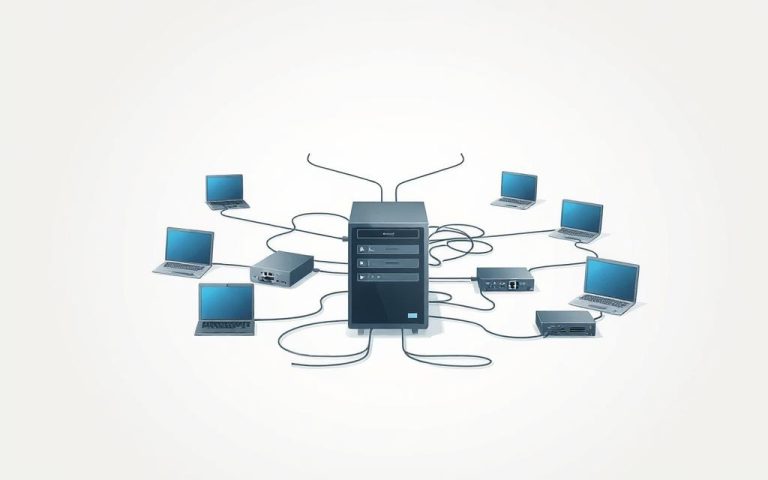
A computer network allows devices to exchange information efficiently. The network functionality relies on protocols that control data transmission3. Devices communicate through wired or wireless connections, creating complex communication systems1.
Network infrastructure includes routers, switches, and servers. These components work together to facilitate seamless data exchange2. Understanding how these elements interact is crucial to grasping computer network basics1.
Different network types serve unique purposes. Local area networks (LANs) cover small areas. Wide area networks (WANs) connect devices across continents1.
These networks support file sharing, internet browsing, and remote collaboration2. Performance and reliability are key in network design. Modern networks aim to minimise downtime and ensure data security1.
The complexity of these systems continues to grow. They support increasingly sophisticated digital communication needs2.
Understanding Computer Networks: Essential Components
Computer networks connect devices and enable seamless information exchange. These systems rely on sophisticated components to transmit data efficiently4.
Network components are fundamental building blocks for digital connectivity. They include crucial elements that facilitate communication across different platforms5.
Network Nodes and Devices
Network nodes are critical connection points within digital infrastructures. These devices include:
- Computers and servers
- Printers and storage devices
- Smartphones and tablets
- Network switches and routers4
IP Addresses and Network Protocols
IP addresses uniquely identify network devices, enabling precise communication5. Network protocols govern data transmission, including:
- TCP/IP: Standardised communication protocol
- HTTP/HTTPS: Web communication standards
- FTP: File transfer mechanism4
Network Infrastructure Elements
Core infrastructure supporting network operations includes sophisticated hardware and software components:
| Infrastructure Element | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Routers | Connect different network segments |
| Switches | Manage internal network communication |
| Firewalls | Provide security and access control5 |
Grasping these network components is crucial. It helps organisations build robust, efficient digital communication systems.
These systems support modern technological infrastructure and enhance connectivity4.
Types of Computer Networks and Their Applications
Computer networks connect devices across various geographical scales. They play a vital role in modern digital communication. Different network types serve unique purposes in small offices and global infrastructures6.

Networks are grouped by their coverage and functionality. This grouping enables smooth data transmission between devices. Understanding network types helps in choosing the right infrastructure for specific needs7.
Local Area Networks (LANs)
Local Area Networks (LANs) connect devices within a limited area. They typically cover distances up to 2 kilometres6. LANs are common in offices, schools, and homes.
These networks offer high-speed data transmission around 100 Mbps6. They’re ideal for private networks and have low-cost setup and maintenance.
- Ideal for private network environments
- Low-cost setup and maintenance
- High data transfer rates
Wide Area Networks (WANs)
Wide Area Networks (WANs) link devices across vast geographical regions. They can span hundreds or thousands of kilometres7. WANs enable global communication by connecting multiple LANs.
These networks support long-distance data transmission6. They’re crucial for international communication but have lower speeds than LANs.
- Connects geographically dispersed locations
- Supports international communication
- Lower transmission speeds compared to LANs
Cloud and Metropolitan Networks
Cloud networks use internet-based infrastructure for flexible connectivity. Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) cover urban areas. They bridge the gap between LANs and WANs.
MANs have transmission speeds from 10 to 100 Mbps6. Cloud networks offer remote access, while MANs support city-wide communication.
- Cloud networks offer remote accessibility
- MANs support city-wide communication
- Adaptable to changing technological requirements
Each network type has unique advantages. These allow organisations to design robust communication infrastructures. They can tailor their networks to specific needs8.
Network Architecture and Design Principles
Network architecture is the blueprint for computer networks. It creates vital communication frameworks for smooth digital interactions9. The OSI model guides data transmission with seven key layers9.
When creating network architecture, organisations must consider important design principles. These ensure the best performance for their networks.
- Scalability to accommodate future growth10
- Reliability and continuous network access
- Robust security mechanisms
- Cost-effective infrastructure management10
Different network models offer unique benefits. Organisations can choose from various options to suit their needs.
- Client-server architecture: Centralised services with dedicated servers9
- Peer-to-peer networks: Distributed systems with equal device capabilities9
- Hybrid networks: Combining multiple architectural approaches9
Modern network design uses advanced technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN). SDN separates control functions and promotes centralised management9.
Cloud-based networks enhance flexibility and provide global accessibility. They don’t require maintaining physical hardware9.
Good network architecture needs ongoing monitoring and planning. This ensures top performance, security, and scalability10.
How Does Computer Network Works: Step-by-Step Process
Computer networks are complex systems of interconnected devices. They enable seamless data transmission across digital landscapes. These sophisticated systems form the backbone of modern digital interactions11.
Networks operate through intricate processes that transform raw data into digital communication. The journey begins by breaking down information into small, manageable data packets. These packets can then navigate through various network pathways12.
Data Transmission Basics
Data transmission involves several critical stages of network routing and protocol communication. Key aspects include:
- Breaking data into small packets
- Assigning unique addressing information
- Selecting optimal transmission routes
- Ensuring secure and reliable delivery
Routing and Switching
Network routing determines the most efficient path for data transmission. Sophisticated algorithms analyse multiple potential routes. They select the fastest and most reliable pathway11.
Software-defined networks enable centralised traffic routing. This provides quick responses to changing network conditions11.
Protocol Communications
Protocol communication ensures smooth interaction between different network layers. These standardised rules govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and reassembled. They maintain the integrity of digital information12.
The magic of computer networks lies in their ability to transform complex digital communication into seamless, instantaneous exchanges.
Modern networking solutions incorporate advanced features like encryption and access control. These enhance data security throughout the transmission process11. The intricate dance of data across network infrastructures continues to evolve.
Network Topologies and Their Implementations
Network topology defines how devices connect and communicate in computer networks. It affects performance, scalability, and reliability. Each topology has unique features that impact network functionality.
The primary network topology configurations include:
- Star Topology: Connects all nodes to a central hub, enabling easy network expansion13. It’s the most common network topology today13.
- Bus Topology: Uses a single backbone cable, good for small networks but less efficient with more devices13.
- Ring Topology: Devices connect in a circle, creating one-way data flow14.
- Mesh Topology: Offers multiple data paths, improving network reliability14.
- Tree Topology: Combines star and bus configurations13.
Organisations must consider performance, security, and costs when choosing a network topology. Each option has its own pros and cons for implementation.
Star topology allows easy troubleshooting and node addition without disrupting the network14. Mesh topology provides strong redundancy but requires more cabling investment15.
Choosing the right topology can reduce energy use and boost data speeds13. Many modern networks use hybrid topologies to meet specific needs14.
Security Measures in Computer Networks
Network security is vital for protecting digital infrastructures from cyber threats. Organisations must implement strong strategies to safeguard their digital assets. Firewalls are crucial in controlling network traffic, with Next Generation Firewalls blocking advanced malware16.
Access control systems are key to network security. They allow organisations to set precise user and device permissions. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) limits user access to essential functions only16.
Multi-factor authentication enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps. This makes unauthorised access much more difficult17.
Data encryption protects sensitive information during transmission. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) detect and prevent various network attacks. These include brute force and Denial of Service incidents16.
Advanced monitoring tools now use artificial intelligence to analyse network traffic. They can identify potential anomalies in real-time before significant damage occurs18.
FAQ
What exactly is a computer network?
What are the primary components of a computer network?
How do different types of networks differ?
What is network topology?
Why is network security crucial?
How do devices communicate in a network?
What is the difference between routing and switching?
Can networks be scaled easily?
What are network protocols?
How do cloud networks function?
Source Links
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-computer-networking/
- https://www.exitcertified.com/blog/the-basics-of-computer-networking-explained
- https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/sysadmin-essentials-networking-basics
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/networking
- https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/networking/articles/what-is-a-computer-network/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-of-computer-networks/
- https://www.lenovo.com/gb/en/glossary/what-is-networking/?srsltid=AfmBOoobIh5ptphAb3elTw97mSlZ6UUOz7z1calkJRaHZSYemhjR04y5
- https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/networking-tutorial/importance-of-types-of-networks-lan-man-wan
- https://www.kentik.com/kentipedia/network-architecture/
- https://nilesecure.com/network-design/what-is-network-design-and-how-to-design-a-network
- https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/computer-networking/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/basics-computer-networking/
- https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-basics/what-is-network-topology
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/network-topology
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-of-network-topology/
- https://www.checkpoint.com/cyber-hub/network-security/what-is-network-security/
- https://sprinto.com/blog/network-security-measures/
- https://nordlayer.com/learn/network-security/basics/